
Statut de conservation
| Menacé |
Description de l'animal
The Lesser Spotted Eagle (Clanga pomarina) is a captivating bird of prey that belongs to the Accipitridae family, which encompasses hawks, eagles, and kites. This species is particularly noted for its elusive nature and distinctive markings, making it a subject of fascination among birdwatchers and ornithologists.Characterized by a moderate size, the Lesser Spotted Eagle typically measures about 55 to 65 centimeters in length, with a wingspan ranging from 145 to 160 centimeters. This bird presents a relatively compact and robust body, with broad wings and a short, square tail, which is essential for maneuverability through its woodland habitat.
The plumage of the Lesser Spotted Eagle is predominantly dark brown, with a paler brown or cream-colored head and neck, creating a subtle yet noticeable contrast. The underparts are lighter, often showcasing spots or streaks, which contribute to its name. Juveniles display a more mottled appearance compared to adults, with more pronounced spots and a generally lighter coloration that gradually darkens with age.
One of the most striking features of the Lesser Spotted Eagle is its intense, piercing eyes, which are yellow to light brown in color, providing a sharp gaze that is essential for spotting prey from considerable distances. The beak is robust and hooked, perfectly adapted for tearing flesh, while the talons are strong and sharp, designed for grasping and subduing its victims.
The diet of the Lesser Spotted Eagle primarily consists of small mammals, such as voles and mice, along with a variety of birds, reptiles, and amphibians. It is a skilled hunter, often seen soaring at low to medium heights over open landscapes or perching inconspicuously in trees, waiting to ambush unsuspecting prey.
Breeding occurs mainly in forested habitats, from lowlands to mountainous regions, with a preference for large, mature forests interspersed with clearings or wet meadows. The Lesser Spotted Eagle is a solitary nester, constructing large nests of sticks in tall trees. Typically, it lays one to two eggs per breeding season, with both parents sharing responsibilities for incubation and feeding the young.
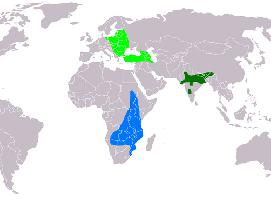
Migration plays a significant role in the life cycle of the Lesser Spotted Eagle. It is a long-distance migrant, traveling from its breeding grounds in Eastern Europe and parts of Asia to wintering areas in Africa. This journey is a testament to the bird's remarkable endurance and navigational skills.
Conservation status of the Lesser Spotted Eagle is of concern due to habitat loss, deforestation, and changes in agricultural practices that threaten its feeding and breeding grounds. Efforts are being made to monitor populations and protect critical habitats to ensure the survival of this magnificent raptor.
In summary, the Lesser Spotted Eagle is a remarkable bird of prey, distinguished by its size, plumage, and hunting prowess. It plays a vital role in the ecosystem, controlling populations of small vertebrates, and its migratory patterns contribute to the biodiversity of the regions it inhabits. Despite facing threats from human activity, the Lesser Spotted Eagle continues to soar across the skies, embodying the wild and untamed spirit of the natural world.
Carte de répartition
Animaux similaires
Nouvelles photos d'animaux
Top 10 des animaux
- Dolphin gull (Leucophaeus scoresbii)
- Diana monkey (Cercopithecus diana)
- Moustached guenon (Cercopithecus cephus)
- Galápagos tortoise (Geochelone nigra complex)
- Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata)
- Stone loach (Barbatula barbatula)
- Russian tortoise (Testudo horsfieldii)
- Greek tortoise (Testudo graeca)
- Common flying dragon (Draco volans)
- Vendace (Coregonus albula)


