
Poids et mesures
| Longueur | de 22 à 23 cm |
|---|---|
| Poids | de 70 à 90 g |
| Envergure des ailes | de 34 à 39 cm |
Statut de conservation
| Intrépide |
Description de l'animal
The Great Spotted Woodpecker (Dendrocopos major) is a medium-sized bird that belongs to the woodpecker family, Picidae. This bird is widely distributed across the Palearctic region, including parts of Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Its striking appearance and distinctive behaviors make it a fascinating subject of study and observation in its natural habitat.Appearance-wise, the Great Spotted Woodpecker presents a striking contrast of colors. Adults typically have black and white plumage with vivid red undertones, making them quite noticeable against the backdrop of their woodland habitats. The back is predominantly black, with white patches on the wings and lower back. The underparts are white, creating a stark contrast. One of the most distinctive features of the male is a bright red patch on the nape of the neck, which is absent in the female. Juveniles can be identified by their red crown, which they lose as they mature. This bird's bill is strong and chisel-like, perfectly adapted for its wood-boring lifestyle. The tail is stiff and acts as a support when the bird is clinging to tree trunks.
In terms of size, the Great Spotted Woodpecker is roughly 23 to 26 cm in length, with a wingspan ranging from 38 to 44 cm. This size makes it one of the larger species within its genus.
The Great Spotted Woodpecker's habitat is largely confined to forested areas, including deciduous and mixed forests, where it prefers mature woodland with a plentiful supply of old trees. These environments provide ample feeding opportunities, nesting sites, and the seclusion this species needs for breeding.
Dietarily, the Great Spotted Woodpecker is versatile, feeding on a wide range of insects and their larvae, seeds, and nuts. Its powerful beak allows it to drill into wood to extract insect prey, and it is also known to visit bird feeders in gardens, particularly in the winter months, where it feeds on suet and seeds.
Breeding season for the Great Spotted Woodpecker begins in early spring. The male initiates the courtship by performing a distinctive drumming display, which involves rapid pecking on a tree trunk or branch to produce a loud, resonating sound that can be heard over long distances. This behavior not only attracts females but also serves as a territorial signal to other males. Once a pair is formed, they excavate a nest hole in a tree, where the female lays 4 to 6 eggs. Both parents share the duty of incubating the eggs and feeding the young.
The Great Spotted Woodpecker plays a vital role in its ecosystem. By excavating nest holes, it not only creates nesting sites for itself but also for other cavity-nesting species that are unable to excavate their own holes. Moreover, its diet helps control insect populations, contributing to the health of forest ecosystems.
In summary, the Great Spotted Woodpecker is a captivating species with a striking appearance and interesting behaviors. Its adaptation to forested environments, diverse diet, and role in ecosystem dynamics make it an essential component of its natural habitat. Despite facing threats from habitat loss and fragmentation in some areas, the Great Spotted Woodpecker remains widespread and relatively common throughout its range, reflecting its adaptability and resilience.
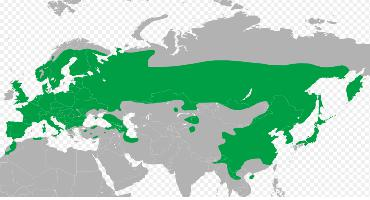
Carte de répartition
Animaux similaires
Nouvelles photos d'animaux
Top 10 des animaux
- Dolphin gull (Leucophaeus scoresbii)
- Diana monkey (Cercopithecus diana)
- Moustached guenon (Cercopithecus cephus)
- Galápagos tortoise (Geochelone nigra complex)
- Russian tortoise (Testudo horsfieldii)
- Stone loach (Barbatula barbatula)
- Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata)
- Greek tortoise (Testudo graeca)
- Common flying dragon (Draco volans)
- Vendace (Coregonus albula)


